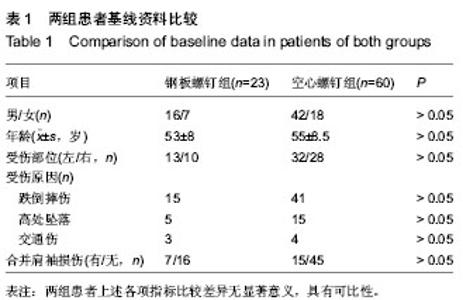
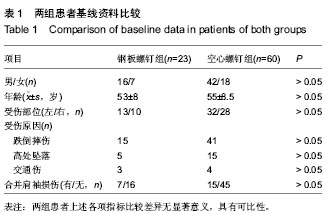
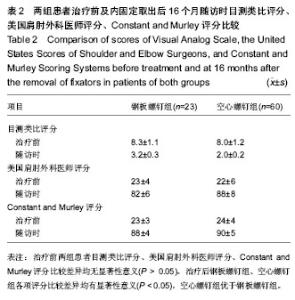
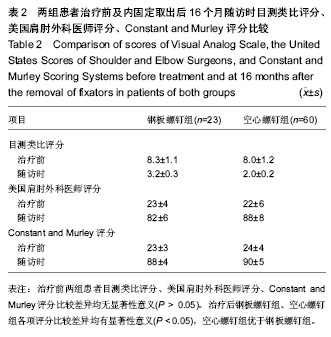
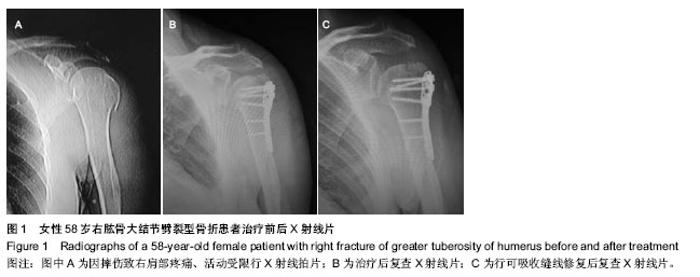
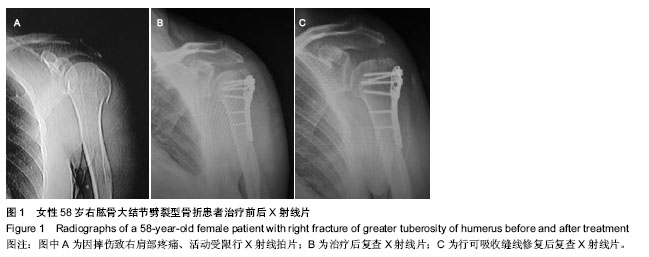
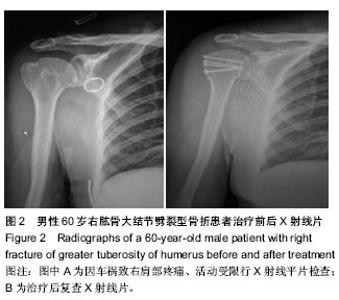
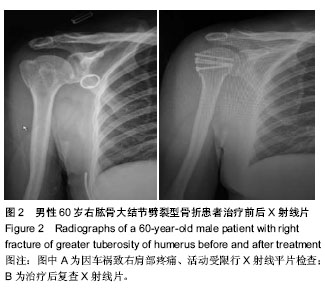
| [1] Mutch J, Laflamme GY, Hagemeister N, et al. Rouleau A new morphological classification forgreater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B:646-651.
[2] 黄强,王满宜,荣国威.复杂肱骨近端骨折的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(3):159-164.
[3] 黄磊,李广旭,李波,等.PHILOS锁定加压接骨板与肱骨近端锁定加压接骨板治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(52):9861-9864.
[4] George MS. Fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2007;15:607-613.
[5] Bono CM,Renard R,Levine RG,et al.Effect of displacement of fractures of the greater tuberosity on the mechanics of the shoulder.J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2001;83(10):1056-1062.
[6] 李国建,许屾,刘祥清.手术治疗移位的肱骨大结节骨折的临床研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2013,7(3):53-55.
[7] Croell MS, Plank RJ. Fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;7:44.
[8] Kannus P,Palvanen M,Niemi S,et al.Rate of proximal humeral fractures in older Finnish women between 1970 and 2007. Bone. 2009;44:656-659.
[9] Gavaskar AS, Muthukumar S, Chowdary N. Biological osteosynthesis of complex proximal humerus fractures: surgical technique and results from a prospective single center trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(5):667-672.
[10] 程兴东,孙强,曾逸文.高龄肱骨近端骨折患者的外科治疗[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(1):33-35.
[11] Platzer P, Thalhammer G, Oberleitner G, et al. Displaced fractures of the greater tuberosity:a comparison of operative and nonoperative treatment.Trauma. 2008;65(4):843-848.
[12] Lill H,Lange K,Prasse-Badde J,et al.T-plate osteosynthesis in dislocated proximal humerus fractures. Unfallchirurgie. 1997; 23(5):183-192.
[13] Gerber C,Schneeberger AG,Vinh TS.The arterial vascularization of the humeral head.An anatomical stray.J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1990;72(10):1486-1494.
[14] 熊进,施鸿飞,王守丰,等.应用内固定锁定系统治疗老年肱骨近端骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(20):1585-1587.
[15] 曾浪清,陈云丰,刘燕洁,等.内侧柱支撑重建在锁定钢板治疗成人肱骨近端骨折中的临床意义[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012, 14(7): 561-565.
[16] 付中国,邓磊,白露,等.肱骨近端骨折锁定接骨板治疗术后并发症分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2011,43(5):666-670.
[17] 方铭,孙贤杰,曹铨,等.锁定接骨板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的近期疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(4):400-401.
[18] Bigliani LU, Kelkar R, Flatow EL, et al. Glenohumeral stability. Biomechanical properties of passive and active stabilizers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):13-30.
[19] Park TS,Choi IL,Kim YH,et al.A new suggestion for the treatment of minimally displaced fractures of the greater tuberosity of the proximal hunerus.Bull Hosp Joint Dis. 1997; 56:171-176.
[20] 张华,倪卫东,高仕长,等.锁定加压接骨板治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2008,24(7):527-530.
[21] 曾浪清,陈云丰,刘燕洁,等.内侧柱支撑重建在锁定钢板治疗成人肱骨近端骨折中的临床意义[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012, 14(7): 561-565.
[22] 方铭,孙贤杰,曹铨,等.锁定接骨板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的近期疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(4):400-401.
[23] Neer CS 2nd. Displaced proximal humeral fractures. I. Classification and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970; 52(6):1077-1089.
[24] Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1987; (214):160-164.
[25] Norouzi M, Naderi MN, Komasi MH, et al. Clinical results of using the proximal humeral internal locking system plate for internal fixation of displacedproximal humeral fractures. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2012;41(5):E64-68.
[26] Jost B, Spross C, Grehn H, et al. Locking plate fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus: analysis of complications, revision strategies and outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(4):542-549.
[27] El-Sayed MM. Surgical management of complex humerus head fractures. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2010;2(2):e14.
[28] Ruchholtz S, Hauk C, Lewan U, et al. Minimally invasive polyaxial locking plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures: a prospective study. J Trauma. 2011;71(6):1737-1744.
[29] 刘印文.手法闭合复位经皮微创固定治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中国骨伤,2012,24(11):949-951
[30] 张德光,刘福金,刘爱华.肱骨近端骨折锁定加压接骨板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2006,22(11):836-838. |